How to Index a Page Fast – A Guide to Unmissable Strategies

Knowing the best practices of how to index a page fast on Google SERP is paramount to surviving on the web.
Indexing a web page quickly on Google can significantly boost your online visibility and engagement. Whether you’re launching a new page or updating existing content, understanding the nuances of indexing and applying proven strategies can make all the difference.
Here, we will talk about the 10 top strategies to index a page fast on Google and drive your web presence.
Understanding Page Indexing on Google
Crawling vs. Indexing vs. Ranking
Before diving into strategies, it’s essential to differentiate between crawling, indexing, and ranking.
Understanding the distinctions between crawling, indexing, and ranking is key to improving your website’s visibility on Google. These processes are interconnected yet distinct stages in how search engines discover, evaluate, and display your content on their results pages.
Crawling
Crawling is the first step where search engines discover your content. Google uses automated bots, known as Googlebot, to “crawl” the web by following links from one page to another.
Crawlers scan the structure and content of your website, looking for URLs to explore. The bot analyzes factors like updated content, changes in site architecture, and new pages.
Usually, when you’ve just published a new blog post and it is internally linked from your homepage or sitemap, Googlebot will likely find it during its next crawl session. If a page is not linked to other content, Googlebot may not find it, which delays or prevents indexing.
Indexing
Once Googlebot discovers a page, it evaluates the content and decides whether it should be included in the Google Index—a massive database of web pages. Indexing involves understanding the page’s context, keywords, multimedia, and overall quality.
During indexing, Google assesses the page’s relevance to search queries. Pages with valuable, unique, and well-structured content are more likely to be indexed.
As per The Capitol Forum, Google has a web index of about 400 billion documents.
For instance, a blog post with well-researched content, a descriptive meta description, and proper schema markup has a higher chance of being indexed. Conversely, a page with thin or duplicate content may be ignored or omitted.
Remember though, indexed pages are not guaranteed to rank. They must still compete based on quality and relevance.
Ranking
Ranking is the final stage where Google determines a page’s position in the search results for a specific query. Only indexed pages can be ranked, and their position depends on several factors like relevance, authority, user experience, and query intent.
Google uses its algorithms, which consider over 200 factors, to rank pages. Key factors include keyword optimization, backlinks, page speed, and mobile usability. Ranking is dynamic and can change based on algorithm updates, competitor actions, or shifts in user intent.
Say, you’ve written a blog post about “best SaaS apps”. Google will analyze your content for keyword relevance, user engagement metrics, and competition. If your content satisfies user intent better than others, Google will rank your content higher. However, you will need to keep an eye on information updates and SERP performances to retain high ranking.
So, now, to get a page indexed fast, you must optimize the first two steps—crawling and indexing—ensuring Google prioritizes your page for inclusion.
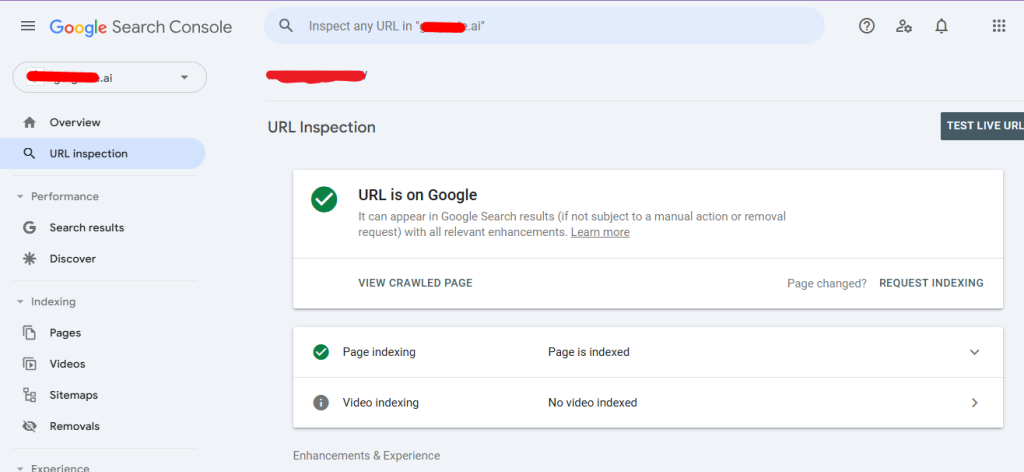
Google Search Console URL Inspection
Google Search Console (GSC) is an indispensable tool for tracking and managing how Google interacts with your website. Using the URL Inspection Tool, you can check if your page is indexed or request indexing for new or updated URLs.
Submitting URL for Indexing
Submitting a URL for indexing is a straightforward and effective way to ensure Google knows about a new or updated page on your website. This process signals Google to crawl and evaluate the page for inclusion in its search index, expediting its appearance in search results.
How to Submit a URL for Indexing?
- Using Google Search Console (GSC), you can:
- Navigate to the URL Inspection Tool in GSC.
- Enter the URL of the page you want Google to index.
- If the URL isn’t indexed, you’ll see an option to request indexing.
- Then, you can request Indexing by:
- After the inspection, click the Request Indexing button.
- Google will queue the page for crawling, and you may see results within a few hours to a few days.
XML Sitemap Submission
An XML sitemap is a structured file that lists the important pages of your website, acting as a roadmap for search engines like Google. It provides essential information about your site’s content, helping search engines discover and crawl your pages efficiently. Submitting an XML sitemap is a vital step to ensure your pages are indexed quickly and accurately.
Creating an XML sitemap is straightforward with various tools and plugins:
- CMS Plugins: If you use platforms like WordPress, plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math can generate sitemaps automatically.
- Online Generators: Tools like XML-sitemaps.com allow you to create a sitemap for smaller websites.
- Custom Development: For highly customized sites, developers can manually generate a sitemap using scripting tools.
If you want to submit your Sitemap to Google, try the following steps:
Upload the Sitemap to Your Website
Place the sitemap in your site’s root directory, typically accessible at https://example.com/sitemap.xml.
Use Google Search Console
- Navigate to the Sitemaps section in GSC.
- Enter the sitemap URL (e.g., https://example.com/sitemap.xml) and click Submit.
- Google will process the sitemap and begin crawling the listed pages.
Verify Submission
After submission, check for any errors or warnings in the sitemap report within GSC. Common issues include broken links, incorrect URLs, or inaccessible pages.
Time Taken by Google to Index Your Page
While Google typically indexes pages within a few hours to a couple of days, the time varies based on factors like website authority, crawl frequency, and content quality. By implementing the strategies below, you can expedite the process.
Strategies That Help to Index a Page Fast on Google SERP
Internal Linking to the New Page
Internal linking is a critical aspect of on-page SEO that enhances the discoverability and visibility of new pages on a website. It involves creating hyperlinks within your website that point from one page to another.
Linking your high-authority pages to new ones serves two primary purposes:
It facilitates crawling and indexing by Search Engines. High-authority pages are often crawled frequently by search engine bots. When these pages include a link to your new page, search engines are more likely to find and crawl the new content quickly.
It distributes Link Equity (SEO Value). High-authority pages carry more link equity, also known as “link juice,” which can boost the SEO performance of the linked page. By linking your new page to one or more such pages, you effectively transfer some of their authority, which can improve the rankings of your new content.
Tips for Effective Internal Linking:
- Use descriptive anchor text which clearly indicates what the linked page is about.
- Place links contextually so that they are integrated naturally within the content rather than isolating them in footers or sidebars.
- Avoid over-linking to focus on quality and relevance to maintain user trust and avoid diluting link equity.
Building Backlinks to the Page
Backlinks, also known as inbound links, are one of the most important factors in improving a page’s authority and visibility in search engine rankings. A backlink is a hyperlink from another website that points to your page, signaling to search engines that your content is valuable and trustworthy.
Building backlinks helps boost the authority. Search engines view backlinks from reputable websites as a vote of confidence, enhancing your page’s domain authority and credibility.
It improves Crawling and Indexing. Backlinks draw Googlebot’s attention, leading to faster discovery and indexing of your page.
It also drives Referral Traffic. Links from high-quality websites can send targeted traffic directly to your page, increasing its reach and engagement.
Link building takes time and effort, much like networking in the offline world. Some strategies you can implement for useful backlinking are:
1. Outreach
Here, you would need to reach out to website owners, bloggers, or influencers in your industry and encourage them to link to your content.
Say, your page features an in-depth guide on sustainable fashion. You can email eco-fashion bloggers to highlight your content as a valuable resource.
2. Collaborations
This strategy includes partnering with other content creators or businesses to create and share content that includes backlinks to your page.
You can co-author an eBook, contribute to a research paper, or host a webinar where your page is linked in the resource materials.
3. Content That Attracts Links Naturally
Another move you can go for is creating high-value, shareable content that other websites will want to link to organically.
Try to publish original research, comprehensive guides, or engaging infographics that become go-to resources in your niche.
4. Directory Listings and Niche Forums
A proven tactic is submitting your page to reputable online directories or participating in discussions on niche forums.
For example, If your page is about “best hiking trails in the Rockies,” try to ensure it’s listed on outdoor adventure directories and shared in relevant forum discussions.
By consistently building high-quality backlinks through strategic efforts, you can enhance your page’s SEO performance, authority, and visibility.
Optimizing Crawl Budget

A crawl budget is the number of pages Googlebot crawls and indexes on your website within a specific timeframe. This budget is influenced by factors such as your site’s authority, size, and technical health.
Ensuring that Googlebot spends its allocated crawl budget efficiently is critical for improving your site’s overall SEO performance and ensuring new or updated content is discovered quickly.
Why Does Crawl Budget Optimization Matter?
Firstly, it ensures Googlebot focuses on valuable pages rather than wasting resources on irrelevant or problematic ones.
Then, it maximizes the chances of your key pages being indexed and ranked effectively.
Finally, for large or eCommerce sites with many URLs, managing the crawl budget ensures even deep pages are crawled.
Steps to Optimize Crawl Budget include:
1. Fixing Broken Links
Broken links (404 errors) waste crawl budget because Googlebot attempts to crawl pages that no longer exist or are inaccessible. By using tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs to identify broken links and either redirect them to the correct pages or remove or replace them in your content.
- Example: If your blog post links to a deleted article, update the link to point to a relevant resource or your own page.
2. Updating Outdated Pages
Outdated pages with stale content may still be crawled, diverting Googlebot from more important pages. In this case, you can regularly audit and optimize your existing content to refresh outdated information. Or, you can merge thin or redundant content into more comprehensive pages.
- Example: If you have a 2021 “SEO Trends” article, update it to reflect the latest trends for 2025, ensuring it stays relevant.
3. Minimizing Duplicate Content
Duplicate content confuses search engines and wastes crawl budget by making Googlebot crawl multiple versions of the same content. You can fix it by:
- Implement canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page.
- Use 301 redirects to consolidate duplicate URLs.
- Prevent unnecessary crawling of duplicate pages with robots.txt or meta noindex tags.
Example: If your website has both “www.example.com” and “example.com” active, set up redirects to consolidate traffic and avoid duplicate crawling.
More advanced techniques for Optimizing Crawl Budget include:
Using Robots.txt
Block crawling of pages that don’t need to be indexed, such as admin pages, login screens, or filters. You can learn more about Robots.txt to get a better grip of the matter.
Prioritizing High-Value Pages
Use internal linking and XML sitemaps to signal the importance of certain pages, guiding Googlebot to prioritize them.
Reducing Low-Quality Pages
Remove or deindex thin content pages, outdated products, or non-performing blog posts to avoid wasting crawl budget.
Optimizing Server Response Times
Improve site speed to ensure Googlebot can crawl more pages within its allocated time.
Creating a Google Web Story
Google Web Stories are short, visually engaging, tappable slides designed to convey information in an interactive format. They appear prominently in Google Discover, search results, and other Google platforms, offering a unique way to showcase content and boost visibility.
So, how do you implement it?
➡️ Choose a Tool or platforms like WordPress (via the Web Stories plugin), MakeStories, or Canva to create your story.
➡️ Focus on Visual Appeal including high-quality images, videos, and concise text to deliver your message effectively.
➡️ Ensure Link to Your Page by adding a swipe-up link or CTA (Call-to-Action) to direct users to your main page.
➡️ Optimize for SEO by adding descriptive titles, alt text for images, and metadata for better indexing.
By integrating a Google Web Story, you engage users with your content, attract search bots to discover your page faster, and drive more users to your page.
LSI Keyword Usage
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords are terms and phrases that are contextually related to your primary keyword. These words help search engines understand the broader context of your content, improving its relevance and visibility in search results.
Suppose your primary keyword is “digital marketing.” Incorporating LSI keywords like “SEO strategies,” “content marketing,” “social media advertising,” and “email campaigns” provides context to search engines, signaling that your page covers multiple facets of digital marketing.
For instance, a sentence might read: “Effective digital marketing involves a mix of SEO strategies, engaging content marketing, and targeted social media advertising to reach the right audience.” This holistic approach ensures your content ranks for a variety of related terms, improving its overall search engine performance. However, the keywords have to relevant and add value to the content.
By including LSI keywords naturally in your content, you ensure it addresses a variety of related queries, making it more comprehensive and engaging for readers. This strategy not only helps with better crawling and indexing but also reduces the risk of keyword stuffing, which can harm SEO performance.
Ensuring Mobile-Friendly Design
Creating a mobile-friendly page is essential for modern SEO, as Google prioritizes mobile-first indexing. This means Google primarily evaluates the mobile version of your site when determining rankings. A site that performs poorly on mobile devices risks losing both search visibility and potential users, as the majority of web traffic now comes from smartphones.
To ensure your page is mobile-friendly, try the following steps:
- Start by using responsive design so your site automatically adjusts to fit different screen sizes and orientations.
- Compress images to reduce file sizes and improve load times without sacrificing quality, as slow-loading pages often result in higher bounce rates.
- Finally, test your site’s mobile usability using tools like Google Search Console (GSC) and Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to identify issues such as small fonts, clickable elements too close together, or content that overflows the screen.
By addressing these factors, you create a seamless mobile experience that satisfies both users and search engines.
Updating the Website Sitemap
A website sitemap is a structured file (usually in XML format) that lists all important URLs on your site, helping search engines understand its structure and discover content efficiently. Keeping your sitemap up to date is essential for ensuring that newly created or updated pages are crawled and indexed promptly.
When you update your sitemap, you provide search engines with a clear roadmap of your site, enhancing the discoverability of recent changes. After making updates, submitting the sitemap in Google Search Console (GSC) is a critical step to notify Google of the modifications quickly.
Suppose you’ve added a new blog post titled “10 Tips for Better Productivity at Work” to your website. To include it in the sitemap, your CMS (like WordPress) may update the sitemap automatically, or you might need to do it manually, depending on your setup.
Once updated, log into GSC, navigate to the Sitemaps section under the Indexing menu, and submit the sitemap URL (e.g., www.example.com/sitemap.xml). This action prompts Google to crawl your site for changes, ensuring the new blog post appears in search results faster.
Regular sitemap updates keep your site well-organized and help maximize visibility for your most recent content.
Sharing on Social Media
Sharing your new page on social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn is an effective way to drive immediate traffic and increase its visibility. While social media shares are not a direct ranking factor for Google, the influx of visitors and engagement they generate can indirectly signal search engines to prioritize indexing the page.
You should also focus on creating tailored posts for each platform. On LinkedIn, write a professional summary highlighting key takeaways and link to the page. On Twitter, share a concise, engaging snippet that relates to your page and include the link to your page. For Facebook, include a visually appealing image and a compelling caption to attract clicks. Each share drives traffic to the page, increasing the likelihood of search engines indexing it promptly.
Sharing on Forums or Communities
Engaging in forums or niche communities like Reddit or Quora can be an effective strategy for driving traffic to your new page while boosting its chances of being indexed by search engines.
By sharing your link in relevant discussions, you not only attract initial visitors but also create contextual backlinks that signal search engines to prioritize crawling your content.
However, the key is to provide genuine value in your responses rather than spamming links, which could harm your credibility and lead to content removal.
Proper Meta Tags Setup
Crafting compelling title tags, well-written meta descriptions, and implementing accurate schema markup are essential steps in improving how Google understands your page. These elements help search engines quickly interpret the page’s purpose and content, enhancing both the speed and accuracy of indexing.
A clear and engaging title tag combined with a relevant meta description also improves your click-through rate (CTR), drawing more users to your site.
If your page is about “Healthy Meal Prep Ideas for Beginners,” an optimized title tag might read: “10 Healthy Meal Prep Ideas for Beginners | Save Time & Eat Better.” The meta description could complement it with: “Discover quick and easy meal prep ideas to kickstart your healthy eating journey. Perfect for busy beginners!”
For schema markup, you could add Recipe Schema to display structured information like preparation time, ingredients, and ratings directly in search results. These enhancements help Google efficiently process your page while making it more appealing to users searching for relevant content.
Definite Pitfalls to Avoid for Page Indexing
Avoiding Duplicate Content
Duplicate content confuses search engines, leading to crawl inefficiencies and lower indexing priorities. Always ensure originality across your site.
Slow Loading Webpages
Google devalues slow-loading pages, as they hinder user experience. Optimize images, leverage caching, and minimize code to improve page speed.
Not Updating Content
Stale content gets deprioritized by Google. Regularly updating pages with new and updated information and content keeps them fresh and encourages faster indexing.
Final Thoughts
Speeding up page indexing on Google isn’t just about submitting URLs; it’s about presenting high-quality, crawlable content that aligns with Google’s standards. By adopting these strategies and avoiding common pitfalls, you can ensure your pages reach audiences swiftly and effectively.
Ready to boost your online presence? Start implementing these tips today!


2 Comments
A very clear and informative discussion on the topic. Thanks!
You are welcome.