Multilingual SEO for Content Optimization in 2025

Quality content optimization to reach wider audiences requires time and effort. However, the job becomes easier and quicker when you know how to implement multilingual SEO.
By localizing and translating your content and website, you can easily communicate with the potential 60% of the global audience that does not search online in English (as per Statista).
So, don’t you think you should capitalize on serving this big segment of the global audience and learn more about multilingual SEO practices? And if you do, join this ride of understanding SEO for global audiences. Let’s begin.
Understanding Multilingual SEO
Multilingual SEO refers to optimizing your website content in various languages. This makes it accessible to users searching in those languages on platforms like Google.
This process helps ensure that your site appears in organic search results for audiences speaking different languages.
For instance, translating and optimizing your English content into French to target users in France is an example of multilingual SEO in action.
By optimizing content for multiple languages, you can expand your reach to international markets. This in turn boosts your chances of converting leads and sales prospects.
In this blog post, we’ll walk you through the process of implementing multilingual SEO to optimize your website content, explaining the best strategies and practices.
Is multi-language good for SEO
Of course! Implementing a multi-language strategy benefits SEO, particularly for businesses aiming to reach a global or multi-regional audience.
A recent Harvard Business Review study showed that 90% of internet users prefer to browse in their native language. See the power of multilingual SEO?
So, let’s look at 7 benefits of multilingual SEO:
Increased Search Visibility
Having content in multiple languages will help you tap into non-English speaking markets. As many people search in their native language, if your content isn’t available in those languages, your site won’t appear in search results when searched in these languages.
Multi-language SEO allows your website to rank in different countries and for various language-specific queries, expanding your reach significantly.
For example, a business offering its content in both English and Spanish can capture searches from the US, UK, and Spanish-speaking countries like Spain and Mexico, increasing organic visibility significantly.
Improved User Experience
Google and other search engines prioritize content that offer a good user experience (UX). When users visit your website and find content in their preferred language, they are more likely to stay, engage with the content, and convert.
Optimizing for multilingual search delivers a more tailored experience, reducing bounce rates and encouraging deeper interaction with your content. This boosts your SERP ranking eventually.
Enhanced Local SEO
Multilingual SEO improves your local SEO efforts. Language targeting SEO translates content and optimizes it for different languages. This helps you rank higher in local searches within specific countries or regions.
Additionally, localized content that is created for the specific cultural and linguistic nuances of the audience, will perform better in local search results.
An example would be a local business in France offering content in both French and English that can attract French-speaking users through local search, while also appealing to international English-speaking customers.
Reduced Competition in Non-English Markets
English-language content dominates the web. Meaning it’s often more competitive to rank for English keywords. However, in non-English markets, there’s generally less competition, allowing you to rank more easily for keywords in other languages.
This is a good multilingual SEO strategy to have that can help you achieve higher rankings and more traffic with relatively less effort.
Remember that: Ranking for a competitive English term might require hundreds of backlinks and years of content development, while the same term in a less competitive language may rank with fewer resources.
Higher Conversion Rates
People are more likely to purchase, sign up, or engage when they can interact with a website in their native language. Multilingual SEO helps you reach these audiences more effectively and can noticeably improve conversion rates as a result.
If, say, you sell products in the German market, providing content in German can improve trust and lead to more conversions than English-only content.
For instance, Nestle is a global company with a dedicated URL “https://www.nestle.com/ “. However, depending on the version of the website, there is a language indicator that indexes the language (and the target location, in some cases) of the page.
If you type in “Nestle Spain” on Google search the following website appears at the top: “https://empresa.nestle.es/es”
Better Compliance with International SEO Best Practices
Implementing SEO for global audiences often involves using technical SEO best practices. This could be using hreflang tags, which inform search engines about the appropriate language and regional version of a page.
This avoids issues with duplicate content (which could arise from having similar content in different languages) and ensures that the right version of your website is shown to the right audience.
The example of Nestle used above is a good example of this.
Increased Organic Traffic
Multi-language website content often gets a boost in organic traffic as they can rank for more search queries across different regions and languages. This broadens your keyword reach and drives more traffic to your site, improving your overall SEO performance.
For instance, if you’re trying to break into the Japanese market, having a site in English won’t help. You’ll need to implement multilingual SEO to translate and optimize the content on your site so Japanese search engines and users can find it.
A website in three languages (English, French, and Japanese) could potentially triple its organic traffic by appearing in search results for all three languages.
How to do multilingual website SEO?
Now that we know the benefits of multilingual content optimization to reach broader audiences across the globe, it’s time to look at the process itself.
1. Conduct Keyword Research for Each Language
Different cultures and languages often have unique ways of expressing the same needs. Simply translating your English keywords won’t always capture the full search intent of users in other languages.
For example, while “cheap flights” may be a popular search term in English, a more colloquial or culturally specific term might be used in another language.
You may use AI content SEO tools like GetGenie AI that can work as a multilingual SEO plugin for WordPress, too. It will help you research and understand keyword volume, trends, and user behavior specific to the language and region you’re targeting.
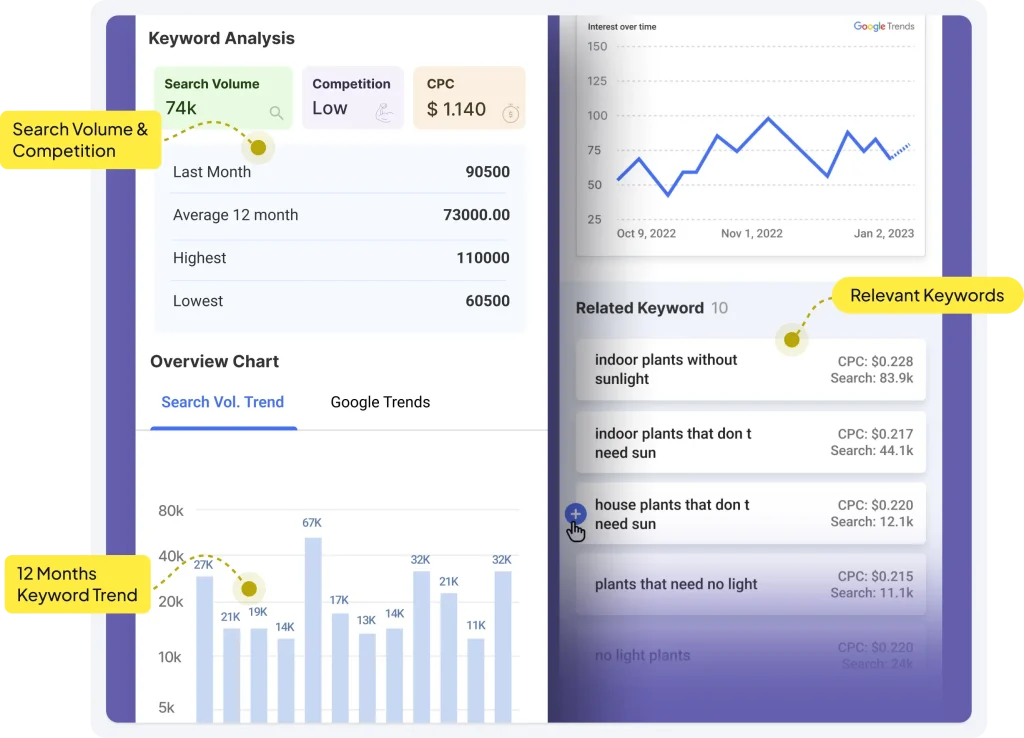
Other tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush can be handy, too.
2. Creating High-Quality Translations (or Localizations)
Avoid Machine Translations:
While tools like Google Translate have improved, they still cannot match the nuance, cultural context, and accuracy of a professional human translator. Poor translations can lead to misunderstandings, reduce credibility, and damage user trust.
Localization vs Translation:
Localization goes beyond just translating words. It involves adapting your content to the target market’s culture, customs, and preferences. For instance, your product descriptions, offers, or blog posts might need to be rewritten to appeal more directly to local tastes.
This could also mean changing visual elements like images, colors, and symbols that might have different meanings across cultures.
Tools like GetGenie are extremely adept at customizing content for customers across various regions and cultures. This strategy makes the user feel more inclined toward the content presented.
3. Using hreflang Tags
Signaling to Search Engines:
hreflang tags are an essential technical SEO element that tells search engines like Google which language and country version of a page should be shown to users based on their language and location.
For example, <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”en-gb” href=”https://example.com/uk/”> would inform search engines to display the UK version of your English page to British users.
Preventing Duplicate Content Issues:
When you have multiple versions of a page in different languages, search engines might see this as duplicate content. Hreflang tags help clarify that these pages serve different audiences, protecting your site from potential penalties.
4. Optimizing URL Structure
There are three primary ways to structure your multilingual website, each with its advantages:
- Subdomains (es.example.com): Subdomains are separate domains but still associated with your main site. They are easy to implement but can be harder to rank due to their separation from your primary domain.
- Subdirectories (example.com/es/): Subdirectories are easier for SEO purposes because they share authority with your main site, making it easier to rank content.
- Country-Code TLDs (ccTLDs) (example.es): ccTLDs are country-specific top-level domains, which send a strong signal to search engines that your site is localized for that country. However, these are harder to manage and maintain, especially if you target multiple countries.

Subdirectories are often the most SEO-friendly solution for smaller businesses, as they allow you to consolidate domain authority. However, for larger companies with dedicated resources, ccTLDs can provide a strong advantage in highly competitive local markets.
But note that, ccTLDs are primarily important for international SEO, not multilingual SEO and show search engines and users that site content is specifically targeted to a certain country or region, but not particularly a language.
5. Localizing Meta Tags and Content
Meta Titles and Descriptions:
Meta tags (like titles and descriptions) need to be localized to include the right keywords for the target audience. These elements play a critical role in helping search engines understand the content of your page and enticing users to click through.
That is why we highly recommend that you have a human translator look at your metadata translations to tune them for better SEO performance in your target language(s).
On-Page Content Optimization:
Just as with meta tags, all on-page content must be carefully translated and optimized with relevant keywords in the target language. This includes:
🟢 headings (H1, H2, etc.),
🟢 internal links,
🟢 product descriptions, and
🟢 blog content.
Remember to also localize alt text for images, as these impact SEO and accessibility. Again, it’s best to have a human editor check the multilingual content.
6. Creating a Multilingual Sitemap
A multilingual sitemap helps search engines discover and index all language versions of your website. It makes multilingual website indexing easier.
Each version of your content should be listed with its corresponding hreflang tag. This gives Google and other search engines a clear map of how your site is structured across languages.
After creating a multilingual sitemap, submit it to Google Search Console and other relevant search engines (like Bing Webmaster Tools) to ensure all pages are properly indexed.
7. Optimizing User Experience
An effective multilingual SEO tip would be to make it easy for users to switch languages on your website by adding a visible and user-friendly language selector. Examples are a dropdown menu or country flag icons. Ensure it is easy to find on every page.
You can automatically redirect users to the correct language version based on their location or browser language settings. However, make sure users can still easily change the language if they prefer to use another version.
Also, since many international users access the web via mobile, it’s essential that your multilingual site structure is mobile-friendly. This includes responsive design, fast loading times, and easy navigation in all languages.

8. Tracking and Analyzing Performance
Using analytics tools like Google Analytics to track the performance of your site in different languages will benefit you in creating robust strategies. Analyze user behavior, bounce rates, conversions, and traffic sources to see how well your multilingual SEO efforts are performing.
Once you are acquainted with the data, use it to gather to adjust your multilingual SEO strategy. If one language version isn’t performing as well as others, you might need to revisit your keyword strategy, translation quality, or on-page SEO elements.
You can utilize AI SEO assistants like GetGenie to optimize keywords and AI SERP analysis.
9. Building Local Backlinks
Just like with SEO in a single language, backlinks are crucial for improving your search ranking. When building backlinks for your multilingual site, try to secure links from authoritative local websites in your target regions.
Partnering with local influencers, bloggers, and media outlets in the target local markets. You can contact them for guest blogging opportunities, press releases, or product reviews.
Sharing content relevant to local news, events, or topics of interest can also boost local link building. Whether through blog posts, case studies, or success stories, these types of content can engage the local community, increasing the chances that they will link back to the information.
Additionally, you can join in local community events for local link building. Whether it’s hosting workshops, webinars, seminars, or joining local business associations or chambers of commerce, engaging in these activities can stimulate interest and encourage local linking on the website.
Differentiating Between International SEO and Multilingual SEO
International SEO and Multilingual SEO are closely related but serve different purposes in optimizing a website for global audiences.
As already mentioned, Multilingual SEO specifically focuses on optimizing your website for different languages to reach audiences who speak different languages.
The goal is to ensure that your website ranks for language-specific searches, making your content accessible to users searching in their native language, regardless of their location.
On the other hand, International SEO refers to optimizing your website to target specific countries or regions, regardless of the language spoken. The focus is on ensuring that your website ranks well in search engines for users in different geographic locations.
International SEO takes into account factors that include:
👉 regional search behavior,
👉 local competition,
👉 cultural preferences, and
👉 geographic targeting.
The Key Focus is Geographic targeting and localization for different regions.
An example could be a company targeting both the US and Australia may create separate pages or websites for each country, using content localized for cultural differences even if the language is the same (e.g., both English for the US and Australia).
Summary of Differences:
| Aspect | International SEO | Multilingual SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Targeting different geographic regions/countries | Targeting users in different languages |
| Targeting Method | Geo-targeting, localization, country-specific domains | Language-specific targeting, content translation |
| URL Structure | ccTLDs, subdomains, subdirectories (region-based) | Subdirectories, hreflang tags (language-based) |
| Keyword Strategy | Country-specific keyword research | Language-specific keyword research |
| Audience | Users in different countries or regions | Users speaking different languages, regardless of location |
| Technical SEO | Geo-targeting, region-specific optimization | Language-targeting, hreflang implementation |
Both International SEO and Multilingual SEO are essential for businesses seeking to expand their reach globally, but International SEO is focused on geography, while Multilingual SEO is focused on language. For global success, many businesses need to incorporate both strategies.
Multilingual SEO Challenges
Implementing the multilingual SEO best practices does not come without its share of difficulties. Let’s look at some challenges that can obstruct your progress in multilingual SEO:
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content is a major challenge for multinational websites, presenting several issues:
Intentional Duplication: For product pages across different languages, such as English, Spanish, and Arabic, duplications are often deliberate. These pages might include unique attributes like pricing, size, or contact details that differentiate them from each other.
Automated Replication: A more complex issue arises when CMS systems automatically duplicate pages for each market. For instance, if a new page is created for the US, the CMS might automatically generate English versions for other markets, even if the product isn’t available or the team hasn’t localized the content.
Often, teams only realize this problem when they see these pages appearing in Google error reports or ranking higher than intended local pages.
Local Site Visibility in Search Results
Search engines aim to present the most relevant results, but sometimes they may display pages from different markets in response to queries.
For example, in Australia, US or UK pages may rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) than the local Australian versions, particularly for brand or product names.
To mitigate this, hreflang tags were introduced to help site owners specify the language and market for each webpage. However, implementing hreflang tags can be challenging, requiring coordination across all markets, including those potentially losing traffic due to cannibalization.
Variations in SEO Processes, Skills, and Focus Areas
Different markets and regions often have distinct priorities, strategies, and expertise, which can lead to conflicts without centralized website governance and SEO management.
Managing multiple agencies, each responsible for specific markets, can further complicate this. Agencies may have varying skill sets and focus areas, with some specializing in technical SEO while others concentrate on content creation or link building.
Summing up
We hope this article has shed light on how to do SEO in other languages and the best strategies for it.
We presented the best practices to implement multilingual SEO despite the obvious complications and challenges.
To make your job easier, you can always take the assistance of AI SEO and content creation tools like GetGenie Ai that come as both WordPress Plugins and SaaS products. Take a sneak peek at GetGenie’s pricing page to know about which package will suit your needs.
