How to Reverse Engineer Competitor Content Strategy
You might be trying to analyze competitor data to improve your own content. Trying to understand what topics they cover and which keywords drive their traffic. And also how their content engages readers. But these will require proper tactics to implement.
This is exactly what reverse engineering competitor content is all about. You need to analyze why your competitors rank well. And also find valuable insights to improve your own content strategy. Then, you can outrank them in search results.
This blog post will help you understand why this approach matters and how to do it step by step.
To reverse engineer competitor content for better SEO results:
➡️ Identify your competitors
➡️ Collect competitor keyword data
➡️ Analyze competitor content & keywords
➡️ Compare content head-to-head
➡️ Do backlink analysis
➡️ Implement findings into your content strategy
Why Reverse Engineering Competitor Content Matters
Reverse engineering your competitors’ content is like getting a cheat sheet for SEO success. The process helps you with:
- Content optimization: Shows you why certain content works so you can replicate and improve upon that success.
- Top keywords: These include the keywords competitors target that resonate with your shared audience.
- Content Gaps: missing content in your website that could be useful to drive traffic
- New Keywords: target keywords to rank for which your competitors aren’t
How to Reverse Engineer Competitor Content Strategy?
Reverse engineering competitor content insights will guide your strategy and help you improve search rankings. The process works as a cheat sheet for SEO performance.
Identify Your Competitors
The first step is to figure out who you should be analyzing. Remember that your business competitors aren’t always the same as your search competitors. In SEO, your real competitors are the websites ranking for the keywords you want, even if they’re in a different industry or sell a different product.
For example, a blog post or informational site might rank ahead of your product page for a keyword. That content or site is a search competitor, even if it’s not from a direct business rival.
You can manually search Google for a few of your main target keywords and note which sites consistently appear in the top results. These repeat performers are your major competitors in organic search.
Collect Competitor Keyword Data
The next step is to gather the keyword insights that powers their content strategy. In other words, what search queries are bringing them traffic?
The most efficient way to get this information is by using dedicated SEO tools like Semrush or Ahrefs. Or specialized tools like GetGenie. With GetGenie, you can create AI-driven, optimized content. Along with analyzing your site content data. Like top-performing pages, keyword data, topical maps, etc.
Using GetGenie, you can collect top-ranking or highly searched keywords related to your topic. If you type in “Top AI Content Tools” and do keyword research using GetGenie, you’ll get 3 different categories of keywords.
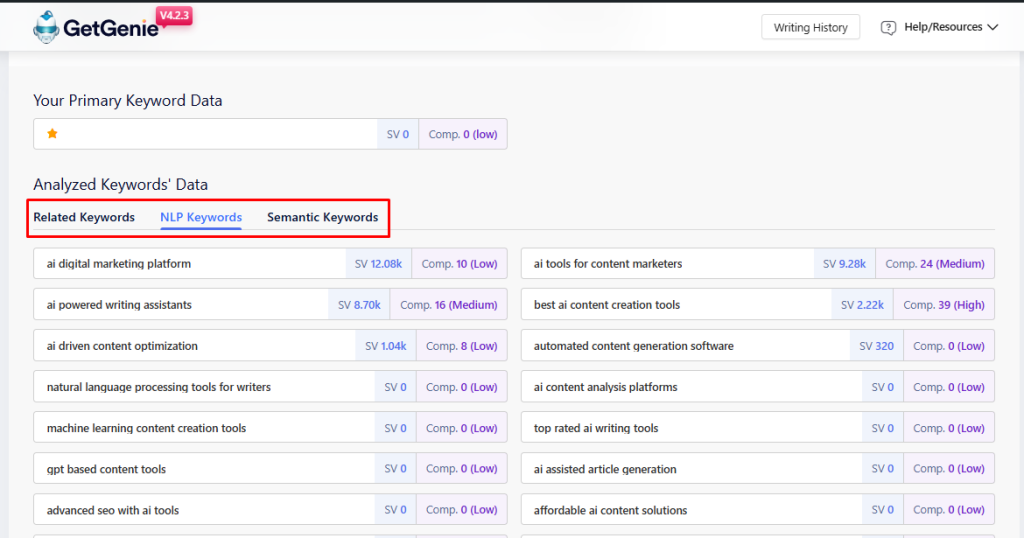
You’ll get insights on Related, NLP, and Semantic Keywords, separately. You can use these to improve your content strategy to rank for those keywords.
Analyze Competitor Content & Keywords
Now that you have the keywords your competitors target, check the keyword’s usage in the content. This step is about studying the competitor pages that rank well and understanding what makes them tick.
Start by examining the top-performing pages for some high-value keywords from your list. Using a tool like GetGenie’s SEO Insights, you can analyze the following quickly and efficiently.
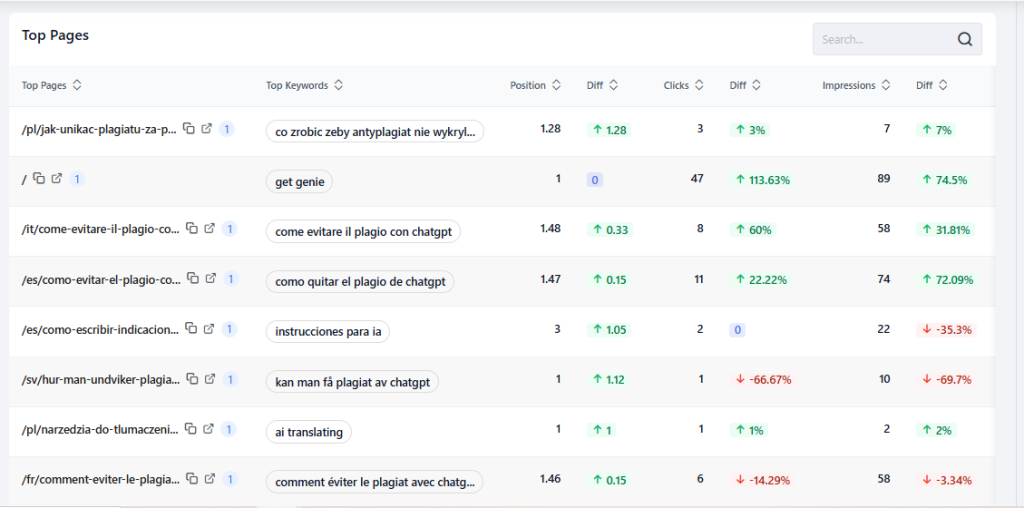
The feature lists top pages for your site, along with comparative positions of the keywords they are ranking for.
GetGenie’s Blog Wizard feature also lets you analyze competitor data to optimize content.
Content format and structure:
What type of content is it (a how-to article, listicle, product page, video, etc.)? How is it organized with headings and sections? A top result will mirror the format that best matches the search intent. It could be a detailed guide for a “how to” query or a comparison page for an “X vs. Y” query.
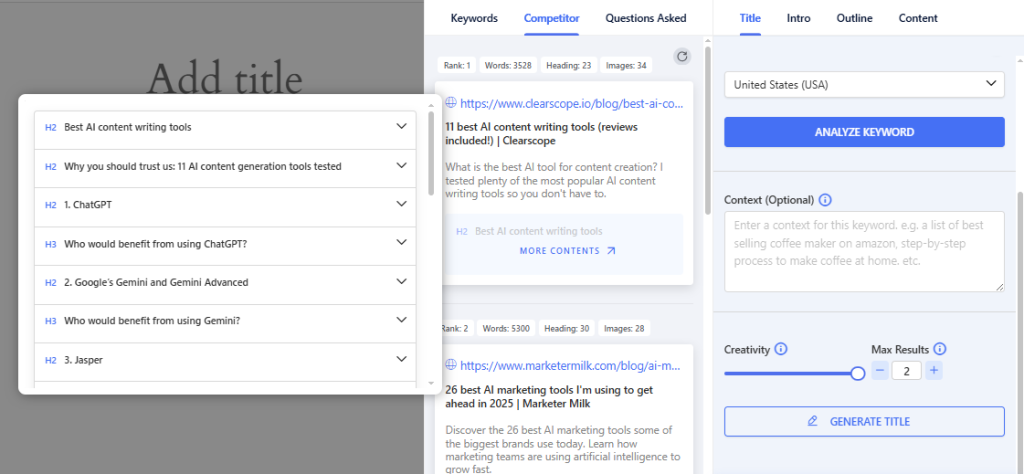
Depth and comprehensiveness:
How thoroughly does the content cover the topic? Does it address multiple subtopics or common questions related to the main keyword? The breadth of coverage is important because Google tends to reward content that fully satisfies the query.
On-page SEO elements:
Check how the competitor uses keywords on the page. Is the main keyword in the title, URL, and H1? Do they use semantic variations and related terms throughout the content? High-ranking pages naturally incorporate the primary keyword and synonyms in a reader-friendly way.
For the keyword “Top AI Content Tools”, GetGenie will show the internal content structure of a competitor. This will help you decide how you will or will not structure your content.
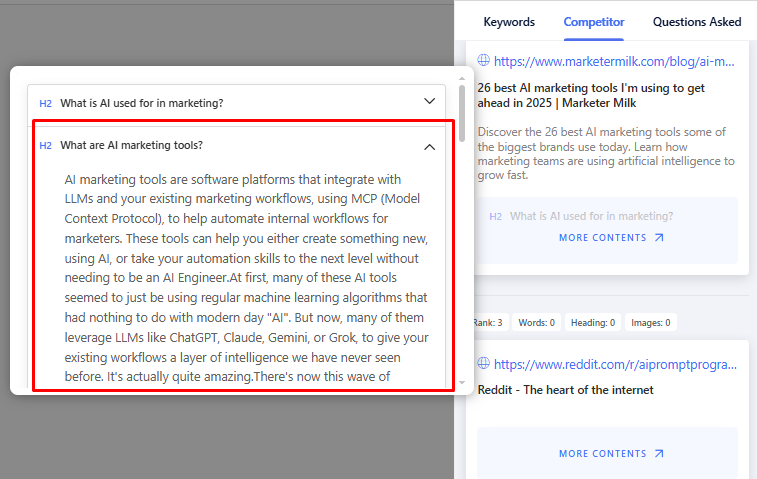
Media and UX features:
Look for use of images, infographics, videos, or interactive elements. These can signal that engaging visuals or media are helping keep users on the page. A page with a helpful infographic or a video walkthrough might be resonating better with the audience.
Compare Head-to-Head
Using reverse engineering, you can compare your site and content head-to-head with your competitors. This comparison will highlight exactly where you’re lagging and where you can outperform.
Tools like GetGenie come in handy when doing this. Its Head-to-Head (H2H) Analyzer helps compare competitor content and find gaps to work on.
When you enter a target keyword using the Blog Wizard and keep the SEO mode turned on, it enables the H2H comparison. The tool will fetch data on the top-ranking pages for that keyword.
It then presents a heatmap comparing how you and your competitors use important keywords and topics. You’ll see your draft (or existing content) side by side with, say, the top 5 or top 10 competitor pages, across a list of relevant terms.
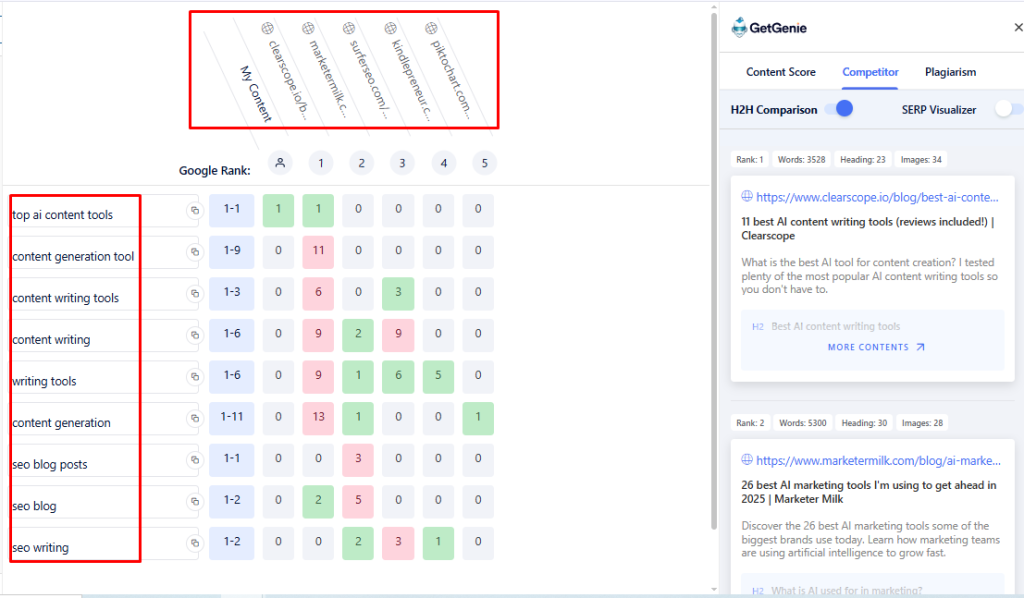
The H2H heatmap uses color-coding to instantly highlight gaps. If a keyword in your content is underused (compared to the optimal range), it might be highlighted in yellow; overused terms are marked red. Green indicates you’re within the ideal range.
As shown above, for the keyword “AI content writer,” the user’s content has used it ideally, once (marked in green). But HubSpot and WordHero’s content have overused it (shown in red). 0 with no color means not used at all
Do Backlink Analysis
High-quality backlinks, links from other sites to a page, remain a top factor in Google’s ranking algorithm. So understanding where competitors get their links will help in content strategy.
Using tools like Ahrefs, Moz Link Explorer, or Semrush’s backlink analysis features, you can pull up the list of backlinks for your key competitors. You should then focus on the backlinks pointing to the competitors’ top-performing content.
As shown below, the Semrush Backlink Analyzer is a good tool to help with backlink analysis.
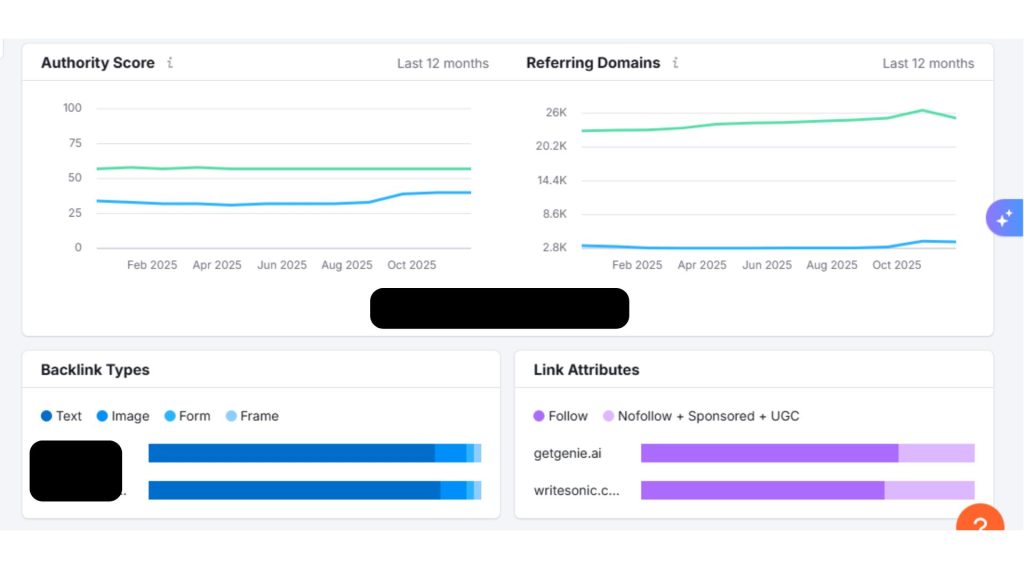
As you review competitor backlink profiles, identify the quality and relevance of sites linking to them. Are they getting links from industry blogs, news outlets, resource pages, or perhaps from guest posts on other sites? Make a shortlist of authoritative domains that appear in multiple competitors’ link profiles. Those are likely important sites in your niche that you should also target.
Implement Findings Into Your Content Strategy
Now that you know what competitors are doing, it’s time to fold those insights back into your own content strategy. Here’s how to put your findings to work:
Fill the content gaps with something better:
For each high-value keyword or topic you’re not covering, plan to create new content to target it. Make this content at least 10% better (or more comprehensive) than what competitors have. If they wrote a “Beginner’s Guide,” you write “beginner-to-advanced mega guide”. If their article lacks examples or data, yours will include them.
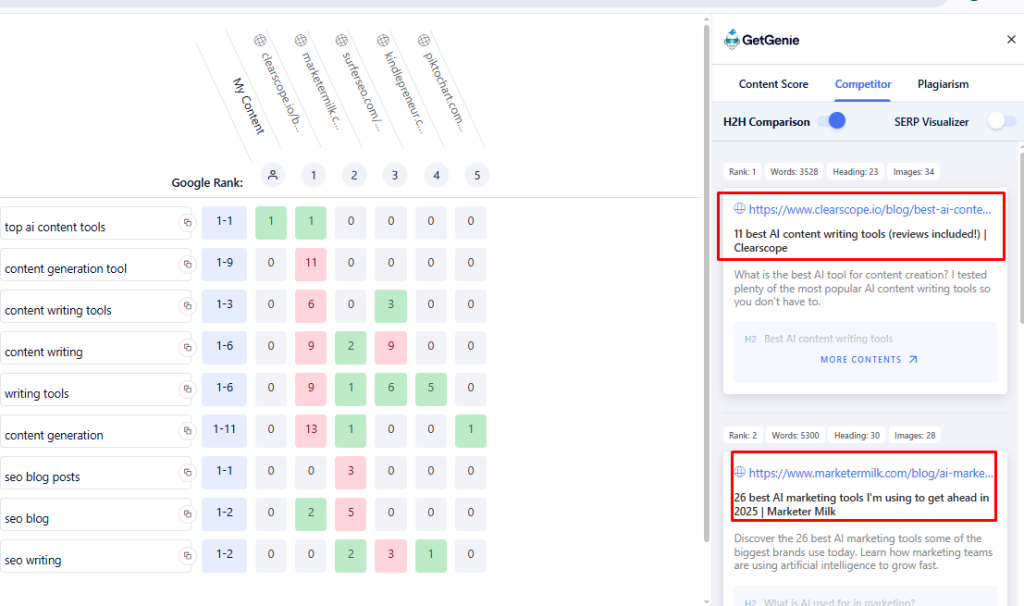
Going back to the keyword “Top AI Content Tools”, you can write “Comprehensive Guide for Top 25 AI Tools” instead of what the competitors wrote above, as shown by GetGenie H2H Analyzer.
Optimize and improve your existing content:
Don’t forget to revisit your current content pieces. These are the pages on your site that are underperforming but just need a boost based on competitor insights. If a competitor’s page on a topic includes an FAQ section with long-tail questions (and ranks well), update your page to answer those additional questions too. Add missing subtopics, add relevant keywords you identified, and ensure on-page SEO basics are covered (better meta title, header). optimization, etc.).
Target long-tail and intent-specific queries:
Your analysis will surface some longer, more specific search queries that competitors are ranking for (or ones they missed that you could own). Add these into your strategy. Long-tail keywords might have lower search volume, but they often convert better and are easier to rank for. For example, instead of just “top AI content tools,” maybe a competitor is killing it with “top AI content tools for remote teams.”
Use internal linking and content structure:
As you add or update content, make sure to improve your site’s internal linking structure. You can take a cue from how competitors organize their content. If competitors have clear content hubs or pillar pages, consider creating your own. Link your related articles together in the right way to help users (and search engines) navigate your comprehensive coverage.
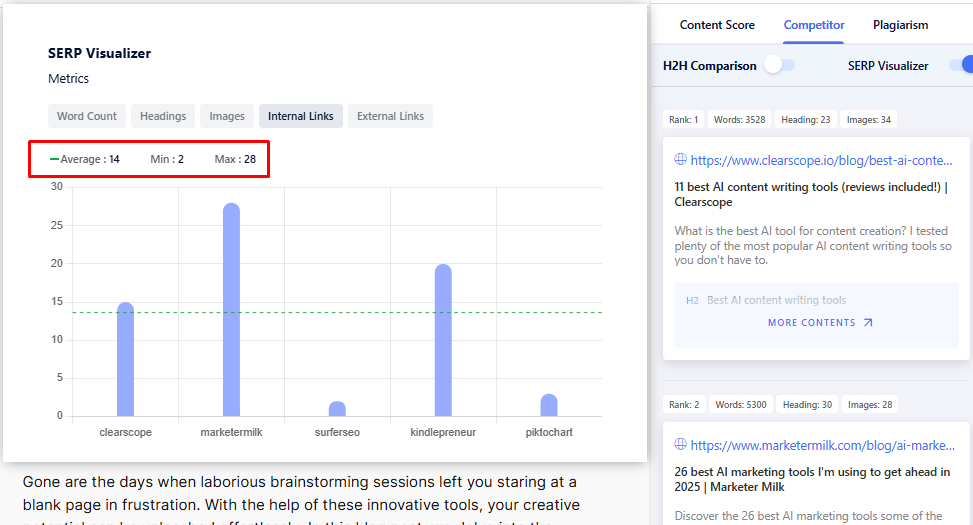
Like here, competing posts for the keyword “Top AI Content Tools” have an average of 14 internal links. As shown by GetGenie’s SERP Visualizer.
Common Mistakes When Reverse Engineering Competitor Content
Reverse engineering competitor content gives you useful insights to work with. But only if you can avoid the following pitfalls.
- Blindly copying competitor moves: Avoid mimicking a competitor’s keywords or content without understanding the context. If you replicate their strategy without aligning it to your own audience and strengths, you will end up with poor content and results…
- Over-reliance on tools and metrics: The data you get from SEO tools provide lots of estimates. Use your ‘common sense’ and analyze what’s happening in the SERP yourself. Don’t obsess over a single metric like word count or keyword density because a tool said so. Consider the bigger picture of content quality.
- Neglecting continuous monitoring: Competitors will continue updating old pages and adding new content. So schedule and plan periodic check-ins on competitor activity for dynamic, ongoing improvements.
- Chasing only high-volume keywords: Overemphasis on volume can cause you to ignore the long-tail keywords that actually drive conversions and are easier wins. Competitors might have overlooked these too, allowing you to capture that segment.
- Forgetting content quality: Remember, great content always wins. If you produce content purely to check the SEO boxes gleaned from competitor analysis and neglect quality, readability, and user value, it won’t perform well. Google’s algorithm (and more importantly, users) rewards content that genuinely helps and satisfies.
FAQs
Summing Up
Reverse engineering competitor content helps you understand what your competitors are doing in detail. You can make informed decisions to strengthen your own content strategy.
Keep in mind that the goal isn’t to follow your rivals, but to outperform them. Use their strategies as a benchmark, then double down on quality, depth, and user satisfaction to create something even better.
As mentioned above, tools like GetGenie will help you improve and expedite the reverse engineering process. So try these out today for optimal results.

