How to Find & Use Related Keywords to Win the SERP Race

A powerful way to top the SERPs is strategically finding and using related keywords. These related keywords include synonyms, variations, and terms closely linked to your seed keyword. They significantly enhance the visibility and relevance of your content in search results.
Here, we’ll explore automated ways and manual techniques of discovering these valuable keywords. Also, we’ll learn how to find & use related keywords to effectively integrate them into your content, optimizing your SEO efforts for better rankings and more targeted traffic.
Ways to Find Related Keywords
You can find related keywords in various ways, either using a tool or manually. Using a sökordsforskning tool will quicken the process and assist in more accurate findings. However, in both cases, you need to do some research and use your own assessment of the findings to list the keywords.
Using a Keyword Research Tool
To make life easy for you, I will show you a compelling way to identify related keywords using GetGenie. Besides being an AI SEO writer and content creation tool, it also helps in providing related keyword searches that you can utilize to create some valuable content.
GetGenie’s Keyword Research feature offers Related Keywords that help search engines recognize the relevance and depth of your content.
These keywords can enhance topical authority and ensure that your pages appear for varied, yet thematically connected, search terms. Also, adding related keywords makes your content more useful to readers.
Först, you need to log in to the WordPress Dashboard and navigate to GetGenie. There, you will find Keyword Research.
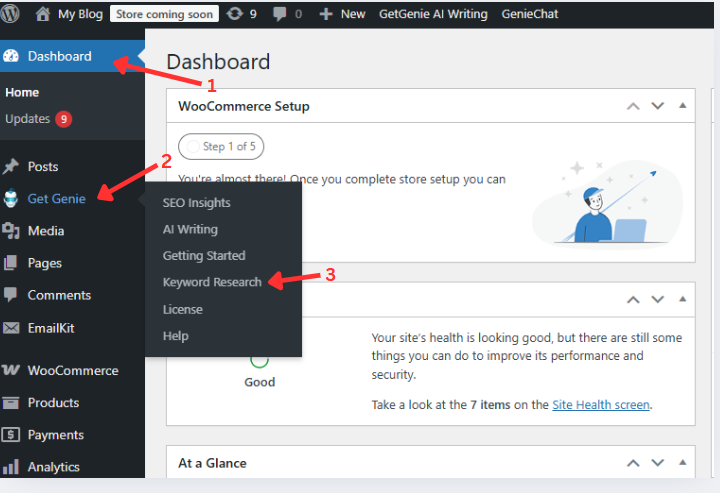
From there, you will enter our Keyword Research platform. You can enter your target keyword, press Analyze Keyword, and let Genie do the rest of the work.
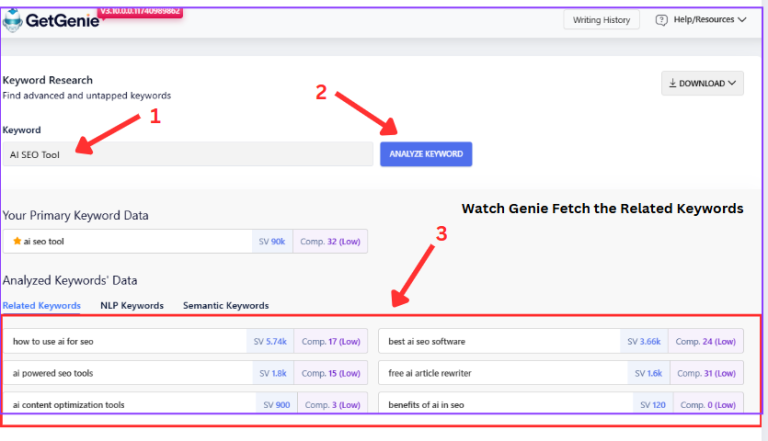
You will get a comprehensive list of related keywords for your seed keyword.
You can use these keywords to optimera befintligt innehåll or create new content that will help you rank faster on SERP.
Finding Related Keywords the Manual Way
If you want to explore other ways to find related keywords, try the following:
| Tactic | How To Perform | Why It Works |
| Google Autocomplete and Related Searches | Type the phrase you are looking for into Google’s search bar and note the suggestions that drop down. After you hit Enter, scroll to the bottom of the results page for “Searches related to…” and check out the list of related keywords. | Autocomplete suggestions come from real, high-volume queries people are typing right now, while the “related” box widens the net to tangential intents. Together, they reveal language your audience actually uses, perfect for headings, FAQ snippets, or secondary keywords. |
| Analyzing Snippets on Google | Skim the blue titles, meta-descriptions, “People Also Ask” questions, and bolded words within each result. Jot down repeating phrases, synonyms, or problem statements. | Google bold-highlights the terms it believes match the searcher’s intent. These clues signal semantic variations you’ll want to sprinkle into sub-headers or supporting paragraphs so your content aligns with how Google interprets the topic. |
| Entering the Page Source | On a top-ranking article, right-click → “View Page Source” (or Ctrl+U). Use the find command to look for <title>, <meta name="”description”">, <h1>-<h3>, and keyword-rich alt text | High performers often optimize their HTML tags with carefully chosen synonyms and long-tails. Extracting them reveals what Google is rewarding on-page and gives you inspiration for your own title tags, headers, and image alt. |
| Doing competitor keyword analysis | Identify 2-3 rival pages ranking for your target query. Read the content and list the recurring terms, section topics, and internal links they target. Tools like GetGenie or MozBar let’s perform competitor gap analysis | Competitors have already done some trial-and-error. Spotting overlaps in their keywords shows which phrases matter for ranking. Gaps point to opportunities to add unique angles or local SEO terms your audience might search. |
How to use related keywords to boost SEO
Now once you have found the related keywords, it’s time to analyze and use them to create or optimize content.
Analyzing keyword search volume
Using a tool like GetGenie, you can view the monthly search volume of a resulting keyword. The search volume is a key indicator of what users are searching for on the internet and to what extent.
Analyzing the search volume, you can place the related keywords on your existing content pieces or the ones you are creating. You can add the keywords in different sections and sentences of your writing. Or write a whole new section that explains the keywords you want your content to rank for.
Usually, you would want to optimize your content for keywords that have high impressions or clicks. For instance, if you search for related keywords for the seed term “marketing automation” using Genie’s Keyword Research feature, your top 3 results will be as follows:
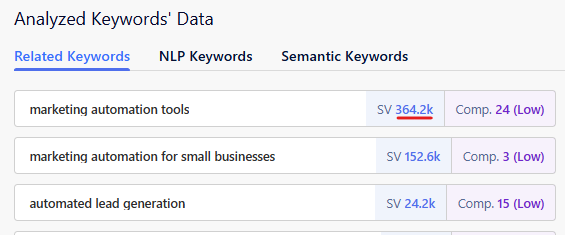
And you want to rank or optimize your content for the related keyword “marketing automation tools” the most, as it has the highest search volume (SV).
Checking keyword difficulty
Another metric you must note and consider is the keyword difficulty or competition level of the keyword. It shows how easy or hard it is to rank for the keyword on the SERP.
Usually, anything below 40 is considered easy to rank for. And anything about 60 is a bit hard to rank for. However, how easily you rank depends on multiple factors that include the quality of your content, page authority, domain authority, backlinks, etc.
High-ranking low-competition keywords
Another tactic for using related keywords in your content page is to go for low-competition nyckelord. A low-competition keyword is a search term or keyword with less websites vying for ranking in search engine results. These are far simpler to rank for but usually have less search volume. This makes them perfect for newer websites or smaller businesses.
For the above example, if “marketing automation” is the target keyword, then a low competition related keyword could be “how marketing automation works in healthcare”. The search term here is very specific and more detailed than a more generic search like “marketing automation”.
If the low competition keyword holds a high rank in the SERP, you should go for it. It means the phrase is getting impressions on the web. And it has a good chance of improving search volume in the future.
Clustering or Mapping Keywords
Before creating content, you should “group” keywords into different topics and pages. Using keyword mapping, you can assign target keywords to specific pages or topics of your site and track them.
Having a keyword map helps you identify:
- new pages to create
- What topics to discuss
- Ways to optimize existing pages
Similar to mapping, sökordsklustring is the process of grouping similar or related keywords into clusters based on their topical relevance.
Using the target search term “marketing automation”, let’s see an example of a keyword map below:
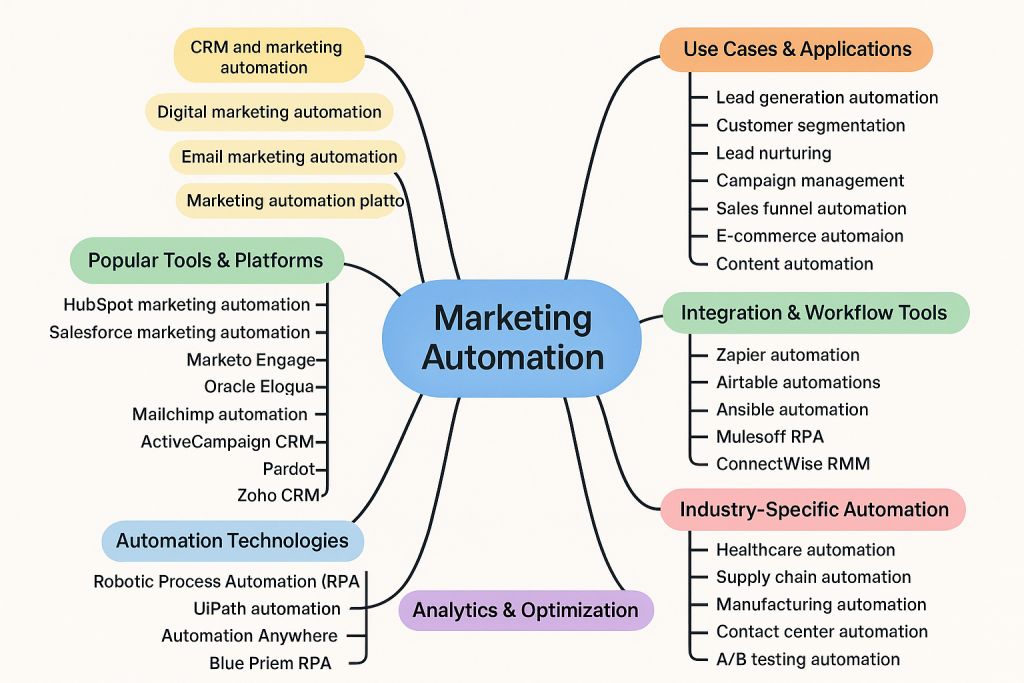
Another type of map that includes topics and subtopics is a topical map. A topical map for SEO is a strategic roadmap for your website’s content strategy. Using it, you can organize your website’s content through a hierarchy of topics and subtopics.
For “marketing automation”, a topical map would look like the following:
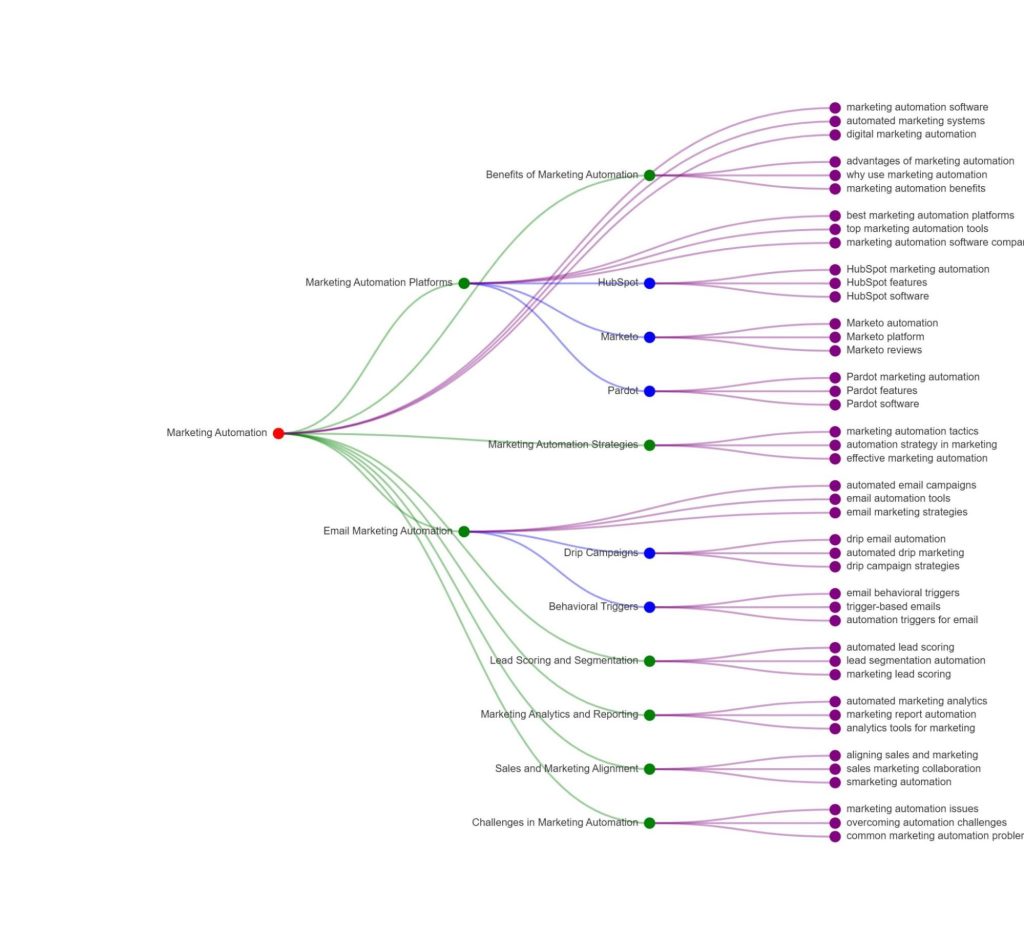
Creating optimized content
Whether you are optimizing existing content or writing new content, placing related keywords in the piece or page is your ultimate use of these keywords. Your content should be of high quality, relevant, and avoid sökordsfyllning.
Plus, you can use AI SEO and content creation tools like GetGenie to craft content in one go with its One-Click Blog generator. Or work your way through using its Anpassat innehåll feature. In both cases, you can edit, rewrite, and optimize the content as per your needs and in a much quicker time than manual writing.
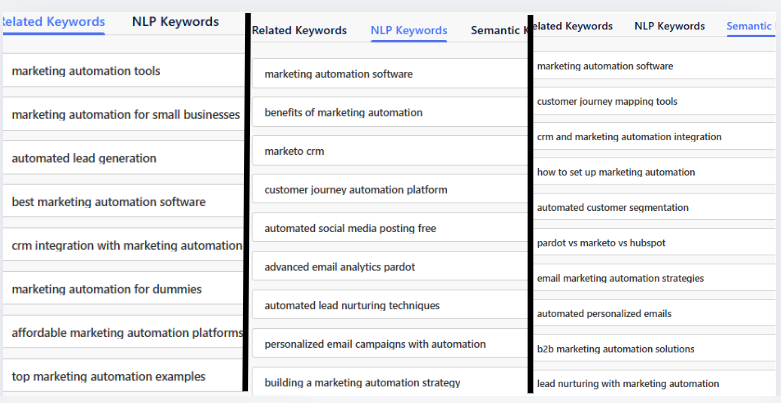
Related vs. NLP vs. Semantic: How the three types of keywords impact SEO
NLP nyckelord are terms that Google’s NLP algorithms identify as important from top-ranking pages & use to understand your content. Semantic keywords are conceptually-connected terms that help provide depth & improve topical relevance. Related keywords are terms commonly searched alongside your main keyword that reflect user intent.
With these varying types of keywords derived from keyword research, you get in-depth lists of phrases that will help you optimize your pages with stronger SEO.
For instance, only using NLP keywords would limit your scope of optimization. Adding semantic keywords to your content and pages would enrich and enhance them.
To differentiate the three, let’s compare their outcomes below for “marketing automation”:
| Related Keywords | NLP Keywords | Semantic Keywords |
How to check keyword relevance
A crucial component of Google Search is keyword relevance. It assists in ensuring that the outcomes that Google displays are pertinent to users’ searches and meet their demands.
Google analyzes user engagement with pages, takes into account precise and relevant keyword matches, and comprehends the purpose behind user queries to assess relevance in search results. Additionally, it considers things like localization, customization, internal linkages, and if the content is current.
5 proven ways to check keyword relevancy are:
- Understanding the search intent: does the audience or user want to buy a product or know more about it?
- Other related content: Are there other associated content types, such as videos and images, based on the keyword?
- Localization: Is the keyword specifically for a particular area or region?
- Personalization: Does the keyword target a specific customer or user type?
- Linking: How well are the keywords linked to other pages or content on the website and to other sources on the web?
Challenges in finding and using related keywords
Finding and using related keywords can have some obstacles that you need to take care of before getting the desired results:
Keyword Stuffing
Sprinkling keywords in your content or webpages won’t get you anywhere if it is not done “naturally” or with proper intent. Just stuffing keywords in places where they sound good to the ears won’t do the trick unless they add value to the content or at least make sense.
You should also keep in mind that keyword stuffing is a big no-no in Google’s policies.
Using Long-tail keywords
Long-tail keywords, or search phrases with 3 or more words and specific intent, usually won’t draw vast amounts of traffic to your site in the early days. As long-tail keywords are low competition and easy to rank for, you should try utilizing them in your content. However, you need to be patient with the results.
Also, regardless of the specificity, difficulty level, and length of the keyword, you should have a mix of short-tail and long-tail keywords for better optimization.
Output variation
When working with SEO tools like GetGenie or UberSuggest, keep in mind that your keyword research results may vary. It is because the dates of the results vary, depending on the tool. For instance, Google Search Console (GSC) shows the most updated results and trends compared to others. However, an advanced tool like Ahrefs might give slower results but more details from different angles.
Language Barrier
Remember, countless users across the globe search for topics and keywords that you can rank for. However, many users DO NOT search in English. 60% of global consumers prefer browsing websites in their native language. And thus, the language barrier dents SEO efforts.
In such cases, multilingual SEO plays a key role. Optimizing your website for multilingual or non-English speakers could help you rank better on the SERP.
Sammanfattning
Whether utilizing advanced tools like GetGenie for efficient keyword research or adopting manual methods such as Google Autocomplete, integrating these keywords thoughtfully into your content can significantly boost your SEO performance.
Focus on keyword relevance, avoid keyword stuffing, try using low competition keywords to your advantage, and leverage techniques like keyword clustering to win the SERP race.

